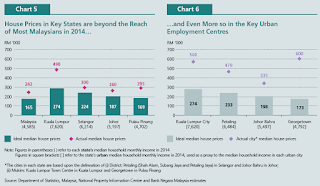
Khazanah Research Institute (badan kerajaan ni) melalui repot pada 24 Ogos 2015 mula membuka bicara. Diulang pula oleh Lapuran Bank Negara 2015, namun siapa peduli?
Terusan dicanang harga rumah sekitar RM500K adalah rumah milik. Bangangnya mereka!
Memang saya marah dengan puak-puak yang menjanjikan langit & bumi setiap 4 tahun nie.
Yang tidak mampu ketika ini, bersedialah dengan 10% deposit untuk rumah idaman anda (buat homework sekarang) kerana rasanya tak lama dah firesale akan kembali.
Tak logik untuk BNM melaung sekuat itu kerana mereka-mereka itu adalah yang terarif dalam hal kewangan!
Untuk yang bersedia, jadikan Rumah oh rumah - Aku mampu memilikimu.